Data Platform/Systems/Superset/Administration
For the public-facing documentation, see Superset.
Superset Kubernetes Readiness Checklist
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Owner | Data Platform SRE |
| Kubernetes Cluster | dse-k8s-eqiad
|
| Kubernetes Namespace | superset-next
|
| Chart | https://gerrit.wikimedia.org/r/plugins/gitiles/operations/deployment-charts/+/master/charts/superset/ |
| Helmfiles | https://gerrit.wikimedia.org/r/plugins/gitiles/operations/deployment-charts/+/master/helmfile.d/dse-k8s-services/superset-next/ |
| Docker image | https://gitlab.wikimedia.org/repos/data-engineering/superset |
| Internal service DNS | superset-next.svc.eqiad.wmnet
|
| Public service URL | superset-next |
| Logs | Superset-next App Logs (Kubernetes) |
| Metrics | Response time and successful requests % |
| Monitors | https://gerrit.wikimedia.org/r/plugins/gitiles/operations/alerts/+/refs/heads/master/team-data-platform/superset-availability.yaml |
| Application documentation | https://superset.apache.org/docs/intro |
| Paging | false |
| Deployment Phabricator ticket | T347710 |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Owner | Data Platform SRE |
| Kubernetes Cluster | dse-k8s-eqiad
|
| Kubernetes Namespace | superset
|
| Chart | https://gerrit.wikimedia.org/r/plugins/gitiles/operations/deployment-charts/+/master/charts/superset/ |
| Helmfiles | https://gerrit.wikimedia.org/r/plugins/gitiles/operations/deployment-charts/+/master/helmfile.d/dse-k8s-services/superset/ |
| Docker image | https://gitlab.wikimedia.org/repos/data-engineering/superset |
| Internal service DNS | superset.svc.eqiad.wmnet
|
| Public service URL | superset |
| Logs | Superset App logs |
| Metrics | Response time and successful requests % |
| Monitors | https://gerrit.wikimedia.org/r/plugins/gitiles/operations/alerts/+/refs/heads/master/team-data-platform/superset-availability.yaml |
| Application documentation | https://superset.apache.org/docs/intro |
| Paging | true |
| Deployment Phabricator ticket | T347710 |
Design
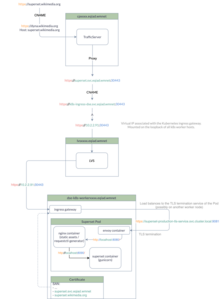
OIDC login
Each superset deployment is configured to let the users log in with our CAS OIDC server, using the WIkitech developer account. The OIDC server returns profile, email, name and group information.
Role mapping
The LDAP groups are mapped to Superset roles:
cn=superset-admins,ou=groups,dc=wikimedia,dc=orggets mapped toAdmincn=wmf,ou=groups,dc=wikimedia,dc=organdcn=nda,ou=groups,dc=wikimedia,dc=orgboth get mapped to thesql_labrole- each user gets assigned the
Alpharole by default - we no longer rely on the
WMF Analystrole, which was custom made and required manual maintenance
This way, everyone at least gets Alpha permissions and sql_lab.
User details update
Whenever a user logs, their Superset user profile is updated with the username, email, first/last name contained in LDAP.
Caching
We deploy a memcached service alongside each superset instance. It is a full-fledged deployment, and not just a sidecar, which allows it to
- survive any superset redeploy, thus persisting the cached data
- be scaled/sized independently of the superset deployments
The following elements are currently cached in this memcached server:
- Dashboard filter state (
FILTER_STATE_CACHE_CONFIG) - Explore chart form data (
EXPLORE_FORM_DATA_CACHE_CONFIG) - Metadata cache (
CACHE_CONFIG) - Data cache (
DATA_CACHE_CONFIG). Note: the cache is isolated by user (whether impersonated or not), through the use of theCACHE_IMPERSONATIONandCACHE_QUERY_BY_USERfeature flags. These ensures that a user who doe not have the right to query certain datasets also can't read the cached values for this dataset.
Static assets serving
Each incoming requests first hit an nginx reverse proxy. It serves all requests for static assets, instead of forwarding them to gunicorn. This is much more efficient, and frees gunicorn worker wall time for actual API requests. All API call are proxy passed from nginx to gunicorn.
requestctl-generator
The SRE team relies on the /requestctl-generator custom endpoint to generate requestctl rules from Superset data. We embed the code for this endpoint in the nginx reverse proxy sidecar, using a ConfigMap mounted via a volume, and serve it using a specific nginx location block. This allows us to make changes to this page quickly, without having to rebuild the statics docker image.
Metrics
Superset itself does not expose metrics. We only collect gunicorn metrics (latency, number of requests by status code), via a statsd to prometheus converter. These metrics are exposed in the Superset (Kubernetes) dashboard.
Alerting
The app isn't running
If you're getting an alert or getting paged because the app isn't running, investigate if something in the application logs (see the checklist section) could explain the crash. In case of a recurring crash, the pod would be in CrashloopBackoff state in Kubernetes. To check whether this is the case, ssh to the deployment server and run the following commands
kube_env superset dse-k8s-eqiad
kubectl get pods
For staging run
kube_env superset-next dse-k8s-eqiad
kubectl get pods
Then you can tail the logs as needed.
If no pod at all is displayed, re-deploy the app by following the Kubernetes deployment instructions.
How to
Deploy the applications
As per Kubernetes/Deployments, we deploy these services from the deployment server, using helmfile. First, ssh onto the deployment server with
ssh deploy2002.codfw.wmnet
superset-next
cd /srv/deployment-charts/helmfile.d/dse-k8s-services/superset-next/
helmfile -e dse-k8s-eqiad -i apply
superset
cd /srv/deployment-charts/helmfile.d/dse-k8s-services/superset
helmfile -e dse-k8s-eqiad -i apply
Exec into the superset container
superset-next
kube-env superset-next-deploy dse-k8s-eqiad
kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get pod -l app=superset -o 'jsonpath={.items[*].metadata.name}') -c superset-staging -- bash
runuser@superset-staging-596cb9cf5-25hvx:/app$
superset
kube-env superset-deploy dse-k8s-eqiad
kubectl exec -it $(kubectl get pod -l app=superset -o 'jsonpath={.items[*].metadata.name}') -c superset-production -- bash
runuser@superset-staging-596cb9cf5-25hvx:/app$
Use the superset cli
Exec into the superset container and run the superset command.
Perform a database upgrade
Exec into the superset container and run the following commands:
superset db upgrade
superset init
Sync the staging database with the production one
When testing a new release in the staging environment it is nice to get the same dashboards as in production, since two different databases are used and they get out of sync very quickly (nobody updates dashboards in staging). The procedure is the following:
# The two databases live on the same mariadb instance
ssh an-mariadb1001.eqiad.wmnet
# Moving to /srv since it is on a separate partition with more free space
cd /srv
# Dump the production db
sudo sh -c 'mysqldump superset_production > superset_production_$(date +%s).sql'
# Get the filename of the production dump
ls -l
# Connect to mysql and drop the staging db
sudo mysql
# Drop and re-create the staging database
drop database superset_staging;
create database superset_staging DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
exit
# Load the production database into the staging one. Change the filename according
# to the dump previously taken!
sudo mysql superset_staging < superset_production_111111.sql
# Then remember that some specific production things need to be changed once superset
# runs. For example, in databases -> presto-analytics (in the superset ui) the kerberos principal
# used is saved in the config and changes between production and staging (the hostname is different).
After that, go to superset-next.wikimedia.org, Settings > Database Connections, and edit the presto connections, by replacing the principal to superset/superset-next.svc.eqiad.wmnet@WIKIMEDIA.

Enable an additional feature flag
If you want to enable a feature flag both in staging and production, add it to charts/superset/values.yaml under config.superset.feature_flags.
If you only want to enable the flag in a single instance, eg staging to test, add it to helmfile.d/dse-k8s-services/superset-next/values-staging.yaml, under config.superset.extra_feature_flags .
Warning: any feature flag under that list will be assumed to be enabled.
Add a specific Superset config flag
If you'd like to add a Superset configuration flag that isn't already covered by the default values and configmap, feel free to add the flag (uppercased) and associated value under config.superset.extra_configuration.
Rebuild the docker images
We build two docker images for Superset: one containing the static assets running a rootless nginx server, and one running the Superset backend, running gunicorn workers.
If you feel the need to rebuild the docker images, make a patch to https://gitlab.wikimedia.org/repos/data-engineering/superset, and the images will be built and deployed once the MR is merged.
Warning: the frontend image might fail to build with an ECONNRESET error (example). This is due to npm install commands being run through a proxy. We're not 100% sure where the error comes from. Some comments found online suggested it's an npm version issue. We've seen improvements by limiting the amount of packages we download at any given time, by installing dependencies by group.The "fix" is to re-execute the pipeline until it passes.
Upgrade Superset
Open a merge request in https://gitlab.wikimedia.org/repos/data-engineering/superset in which you change the Superset tag fetched during the docker image build. Once merged, the image will be built and published to our docker registry. Find the publish gitlab jobs, and find the tag containing production-frontend or production-backend (example). Once you have the new tag for both the frontend and the backend, update the app.version and assets.version values in the superset helmfile value files, create a change request on deployment-charts. Once merged. redeploy the staging and production superset services and then perform a DB upgrade.
Test a different role's permissions
During a couple of superset upgrades, there have been permissions removed from the Alpha role, which causes our users to see errors, sometimes, frustratingly, "unknown error" (at least by looking in the network tab you can see 401 unauthorized status).
It's theoretically possible to create test users, I don't have a method to do so currently so instead I modify my user to have the role I want to test. I do so in the superset app shell; other database operations could be done manually this way.
Exec into the superset container, and start a superset shell:
runuser@superset-staging-596cb9cf5-25hvx:/app$ superset shell
Loaded your LOCAL configuration at [/etc/superset/superset_config.py] ...
>>> app
<SupersetApp 'superset.app'>
The database connection is accessible under app.extensions['sqlalchemy'].db.session:
>>> session = app.extensions['sqlalchemy'].db.session
>>> from flask_appbuilder.security.sqla.models import User
>>> me = session.query(User).filter_by(username='razzi').first()
>>> me
razzi -
>>> me.roles
[Alpha]
# You can modify roles as follows:
>>> Role = me.roles[0].__class__
>>> session.query(Role).all()
[Admin, Alpha, Gamma, granter, Public, sql_lab]
>>> [admin, alpha, *roles] = session.query(Role).all()
>>> me.roles.append(alpha)
>>> me.roles.remove(admin)
>>> session.add(me)
>>> session.commit()
At this point I'd have alpha and not admin roles (this can be confirmed by going to your superset profile) and I can test what other Alpha users see.
